

- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
EPILEPSY WITH MYOCLONIC ATONIC SEIZURES (EMAtS)
Background
The background is normal at onset. Biparietal monomorphic theta rhythms may be seen. With increased seizure frequency, generalized slowing may be seen.
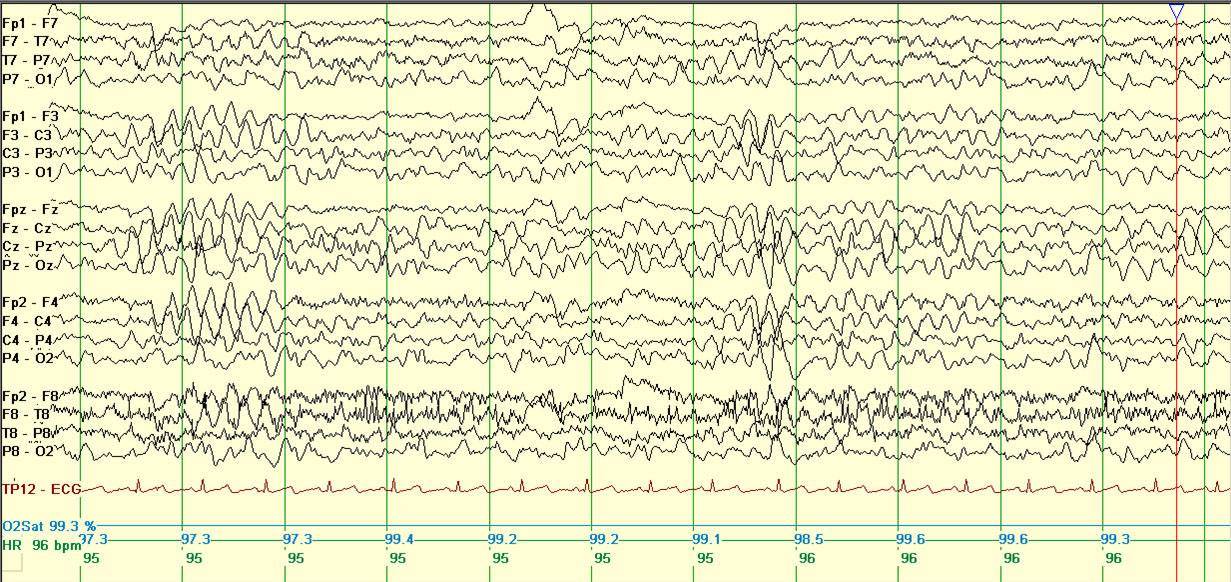
Example of bi-parietal theta.
CAUTION Focal slowing
consistently over one area  consider
structural brain abnormality.
consider
structural brain abnormality.
Interictal
2-6Hz generalized spike- and polyspike-wave is seen.
CAUTION Generalized paroxysmal fast (≥10Hz) activity in sleep  consider Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
consider Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Activation
Hyperventilation may elicit generalized spike-wave and absence seizures (if present clinically), photosensitivity is rare.
EEG abnormality is enhanced by sleep deprivation, in drowsiness and in sleep. Generalized spike-wave often becomes fragmented with sleep deprivation or in sleep. Fragmented generalized spike-wave can appear focal or multi-focal but usually is not consistently seen in one area. The morphology of the focal spike-wave typically appears similar to the generalized spike-wave.
CAUTION If photoparoxysmal response at low flash frequency  consider CLN2-disease.
consider CLN2-disease.
Ictal
The myoclonic component of a myoclonic-atonic seizure is associated with a generalized spike or polyspike. The atonic component is associated with the aftergoing high voltage slow wave. During non convulsive status, the EEG shows long runs of high amplitude 2-3Hz irregular generalized spike-wave with background slowing.