- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
GANGLIOGLIOMA
Imaging
Imaging for optimized detection of ganglioglioma:
MRI should include thin slice volumetric T1-weighted images, axial and coronal T2-weighted and FLAIR images.
Imaging characteristics of ganglioglioma:
The appearance of a ganglioglioma can vary due to variable growth patterns, but may include:
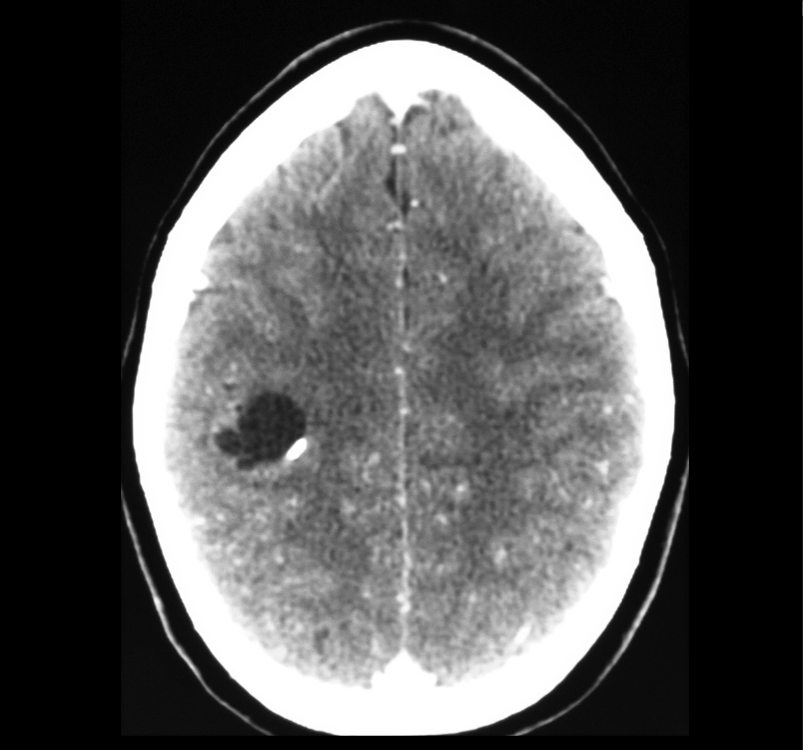
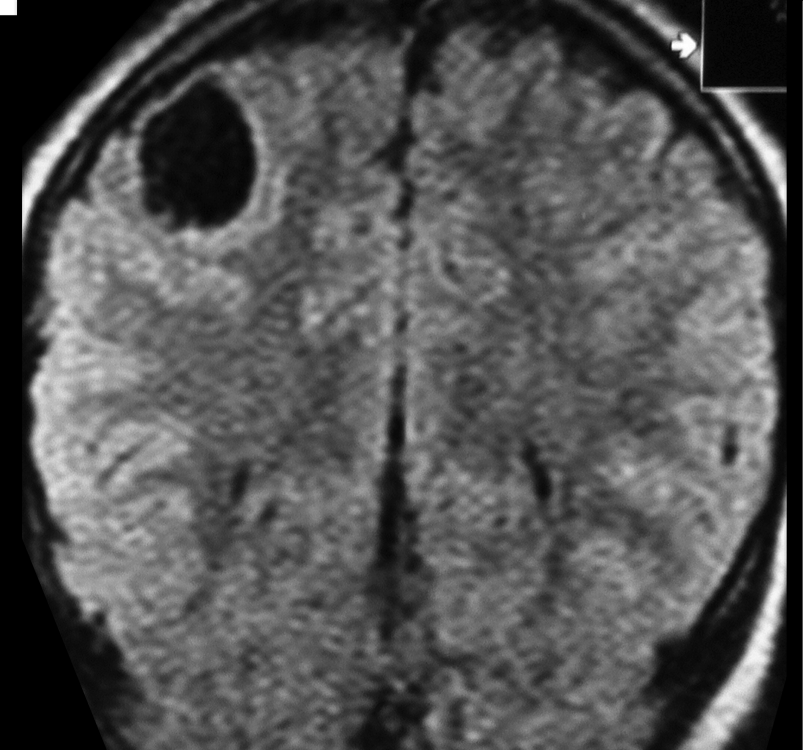
- Either a partly cystic abnormality, with an enhancing mural nodule or a solely solid abnormality (which may expand an overlying gyrus)
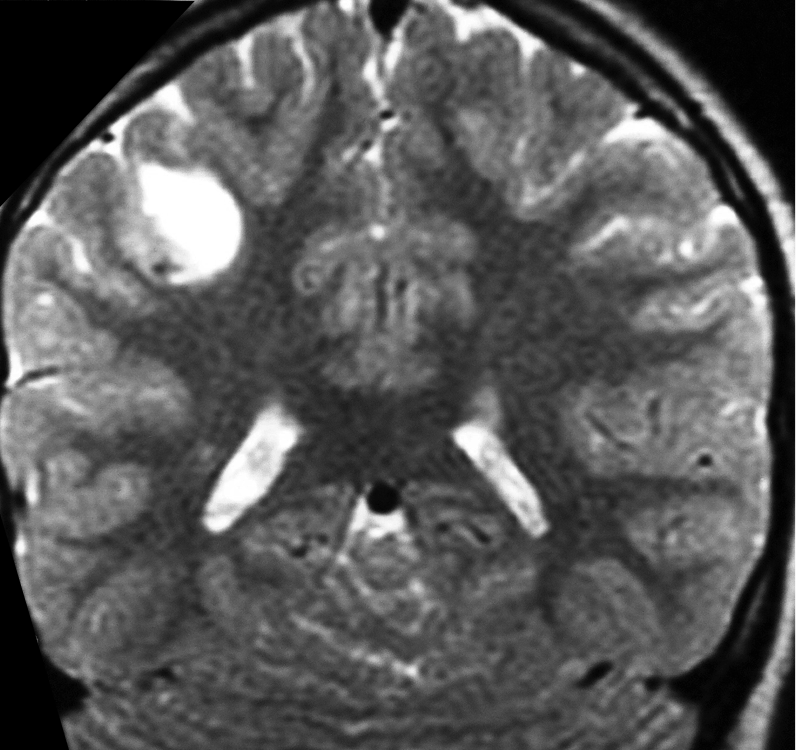
- Solid components that are iso- or hypointense on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2-weighted images
- Solid components that enhance commonly (~50%)
- Areas of calcification, that are commonly seen (>30%, seen on CT or T2* weighted MR imaging)
- Scalloping of the inner table of overlying skull bone, without actual skull bone erosion
- A distinct absence of peritumoral edema (on T2-weighted images/FLAIR)
Gangliogliomas can co-occur with focal cortical dysplasia and/or with hippocampal sclerosis.
Imaging of a ganglioglioma
The images show a CT, T2-weighted and FLAIR image of a ganglioglioma, with a cystic component and an enhancing mural nodule, seen on the contrast CT image.